Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection (DI) is a software design pattern that helps us provide objects (dependencies) that a class needs, without creating them manually inside the class.
Think of it like this 🤔
If a class needs a tool (like a hammer), instead of building the hammer itself, someone gives it the hammer ready to use.
Why Use DI?
Keeps code clean and testable
Reduces duplication
Follows the principle of loose coupling (classes depend on abstractions, not on concrete implementations)
How it works in .NET Core
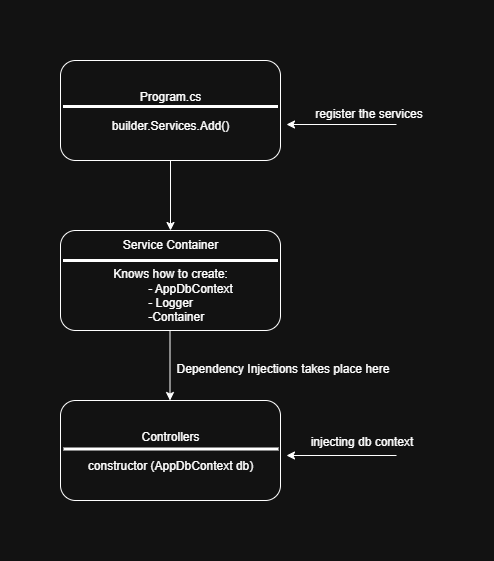
ASP .NET Core has built-in DI Container. Just the same way we registered the DbContext, the DI tells the system "When someone asks for an
AppDbContext, here’s how to create it."Later, when your app needs that
AppDbContextin a class (e.g., a controller or service), you don’t create it manually — the system automatically injects it for you.An example is registering AppDbContext with the InMemory Database. It will register AppDbContext as a service. It then tells the system to use in-memory database when creating AppDbContext.
Later when we shall be creating a class, here how the DI is injected.
You do not have to use "new AppDbContext(...)" because the framework injected it automatically.
Terms to Remember
Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
Dependency | An object a class depends on (e.g., |
Injection | Supplying the dependency from outside |
Service Container | Built-in system in .NET Core that holds all registered services |
Register | Telling the container how to create a dependency |
Resolve | The container gives you the dependency when needed |
Summary
How does AppDbContext work with Program.cs?
AppDbContext tells EF that you want to work with a table of Event objects (a database table)
Program.cs registers AppDbContext with the built-in Dependency Injection (DI). This tells the app that "Whenever someone needs AppDbContext, give them an instance that uses an in-memory database called EventDb "
In-memory database is used for testing and learning as it acts as a fake database stored in memory (RAM), so no actual SQL server is needed
When Program.cs registers AppDbContext, you can inject it in any part of your application. We will explore this when we write CRUD operations of our Minimal API